Accidental Overdoses of Injected Weight Loss Drugs Are Surging
[ad_1]
Poison control centers across the country are fielding more and more calls for help related to accidental overdoses of semaglutide, the active ingredient in Wegovy and Ozempic, the new injected drugs for weight loss and diabetes.
There have been almost 3,000 calls related to semaglutide this year, according to data tracked from January through November of 2023 by America’s Poison Centers. That number is nearly double the amount reported in 2022. Altogether, calls related to semaglutide have surged roughly 1,500 percent since 2019.
“I believe calls are increasing because the overall use of the medication is increasing,” says Julie Weber, a registered pharmacist and director of the Missouri Poison Center and a board member of America’s Poison Centers.
Semaglutide Overdose Can Cause Serious Gastrointestinal Issues
Most often overdoses related to semaglutide cause gastrointestinal issues like nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain, Weber says. Some people also experience headaches, dizziness, or shaking.
But in rarer, more serious cases, people can experience severe vomiting that leads to extreme dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. “If left uncorrected, this could be life threatening,” Weber says.
Accidental overdoses of semaglutide have surged in recent years as more injected drugs containing this ingredient have come on the market to treat diabetes and aid weight loss. Ozempic, the first drug in a family of medicines known as GLP-1 agonists that contain semaglutide, was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2017 to treat type 2 diabetes. Two years later, the FDA cleared another drug made with semaglutide, Wegovy, for weight loss.
“Unintentional medication errors account for most of the increase in reported cases to poison centers,” says Gary Smith, MD, DrPH, director of the Center for Injury Research and Policy at Nationwide Children’s Hospital.
Ozempic and Wegovy Dosing Errors
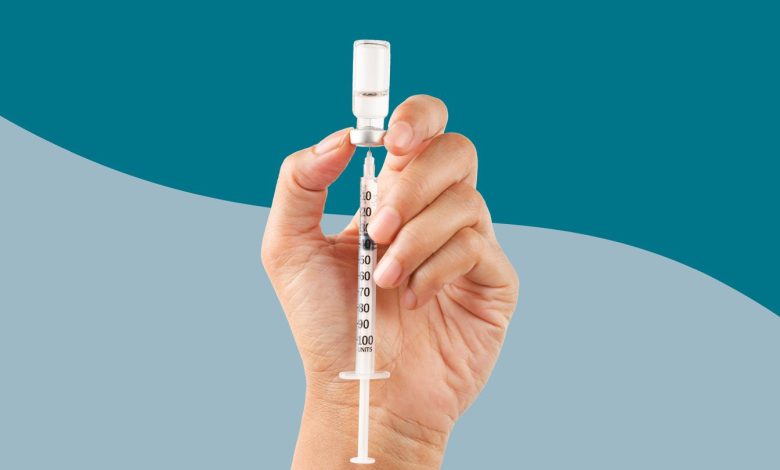
Ozempic and Wegovy are sold as pens that can inject a preselected dose, which should limit the potential for accidental overdoses, says Joseph Lambson, PharmD, director of the New Mexico Poison and Drug Information Center in Albuquerque.
“That being said, overdose is possible with pens that can provide different doses if patients select the incorrect dose,” Dr. Lambson says.
Persistent short supply and high demand for Ozempic and Wegovy may also be indirectly contributing to some accidental overdoses, Lambson says. That’s because shortages are leading more people to seek out compounded forms of semaglutide, which are sold in vials and require people to use a needle and syringe to draw up the correct dose to inject on their own, Lambson.
“It is more common for patients to experience dosing errors when drawing up their own medications compared to pre-filled pens or syringes,” Lambson says. “This, in addition to the popularity of the drug, is most likely contributing to the increased call volume we are experiencing.”
In New Mexico, poison centers have fielded some calls from patients who unintentionally took a double dose of semaglutide, injected the medicine too soon after their previous dose, or who misunderstood the dosing instructions, Lambson says. While no one has died, 43 percent of the people who called about accidental semaglutide overdoses did require immediate medical attention.
What to Do if You Think You’ve Taken Too Much Semaglutide
Symptoms of a semaglutide overdose like nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain can be normal side effects of Ozempic and Wegovy that develop even when people take the drug as prescribed. Weber advises anyone who experiences these symptoms and isn’t sure what to do should contact their health care provider or call their local poison control center at 800-222-1222.
“By contacting the poison center, a medical expert immediately is available to help evaluate whether medical care should be sought or provide guidance for home observation,” Weber says.
[ad_2]




